
The skin is the largest organ in the system, and it is a critical and sophisticated organ that completely covers the body. Skin disorders are illnesses that affect the surface of your skin. Rashes, irritation, itching, and other skin abnormalities may be caused by several disorders. Some skin disorders are caused by genetics, while others are caused by lifestyle factors. Medications, lotions, and ointments, as well as lifestyle modification, may be used to treat skin diseases.
People of all ages and colours suffer from skin diseases. Because your skin is the largest organ in your body, it is constantly exposed to many elements that can cause rashes, allergies, and skin disorders. Because skin illnesses often have similar symptoms, it’s difficult to tell which one you’re dealing with.
The type and severity of skin problems vary widely. They might be transitory or permanent, and they can be pleasant or unpleasant. Some are caused by circumstances, while others may be inherited. Some skin disorders are trivial, while others are potentially fatal.
Let’s have a look at the most common skin disorders their cause and treatments:-
Acne
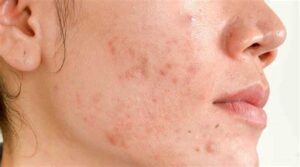
For every youngster, acne, the most common skin problem, could be a cause of anxiety. Acne is also becoming more common among adults.
Acne is a skin condition caused by clogged hair follicles and oil glands (sebaceous glands), which are frequently provoked by hormonal fluctuations. Acne encompasses not only pimples on the face, but also blackheads, cysts, and nodules.
Cause
- Sebum or excessive oil production
- Dead skin cells accumulating
- Infection of the follicle with bacteria
- Hormonal changes that occur during puberty or pregnancy
Treatment
- Skincare is so vital that you could not achieve the results you want if you don’t take care of it. Even if you apply your acne treatment correctly, if you are too hard on your skin, fresh outbreaks may form. To get rid of acne, you’ll need to use moderate skincare.
- If you have severe acne, you should see a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis.
Atopic dermatitis
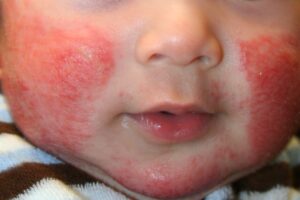
Amongst the most frequent types of eczema in kids is atopic dermatitis. Although the specific aetiology of atopic dermatitis is unknown, experts believe that genetics, the surroundings, and/or the immune response may all have a role.
Atopic dermatitis can affect the face, hands, and feet, as well as the creases and folds of the skin. Skin that is dry, scaly, and itchy is common, and repeated scratching can result in a thicker region.
Cause
- Although the specific aetiology of eczema is unknown, it is linked to an overactive immune system.
Treatment
- Consult with your doctor, who will work with you to build a treatment regimen that may involve one or more of these alternatives.
- Omega-3 fatty acids, for example, are anti-inflammatory meals (present in fatty fish)
- Foods high in quercetin, such as broccoli, blueberries, and cherries.
Sunburn

Sunburns happen when the skin is exposed to too much ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun or sunlamps. The skin becomes red, irritated, and heated to the touch, and it may even scrape away. Albeit with sunscreen treatment, it’s difficult to tell how much time in the sun is suitable. Sunburns that occur frequently, particularly as a youngster, can increase the risk of skin cancer in the future.
Cause
- The major cause is excessive exposure to sunlight lacking sufficient protection. The sun’s UV rays cause skin reactions such as an increase in melanin production, which causes skin darkening, and an increase in histamine production, which causes inflammation.
Treatment
- Applying an icepack to the affected area
- Aloe vera application on the affected area
- Using a moisturiser regularly
- Cleaning the afflicted area and applying sunscreen
Rosacea
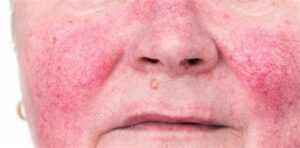
Light-skinned people are much more likely to get this skin disorder. People who blush or flush red in the skin are more likely to be impacted. Rosacea starts as redness around the nose and cheeks and can progress to pimples if left untreated. Excessive cell development could sometimes result in a nose protrusion.
Cause
- Rosacea is caused by an increase in blood flow to the skin’s surface. The specific aetiology is unknown, however, it is thought to be a combination of inherited and environmental factors.
Treatment
- Rosacea has no known cure. The goal of treatment is to reduce the signs and symptoms. The length of treatment is determined by the kind and severity of the symptoms. Medication, laser therapy, and lifestyle changes are all part of the treatment plan.
Cold sores
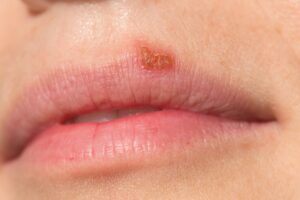
Cold sores can be found around the mouth and in other parts of the face. They’re usually red, fluid-filled blisters. They only appear on the nose, fingertips, and within the mouth in rare cases. In the patches, they are frequently converged. Cold sores can last for 14 days or longer on the skin.
Cold sores are caused by a common virus known as herpes simplex. They can be passed from one person to the next by intimate contacts, such as kissing. Even if the sores are not visible, they can readily spread.\
Cause
- HSV-2, the virus that causes genital herpes, can also transfer to the mouth and produce cold sores during oral intercourse.
Treatment
- In severe situations, antivirals in the form of oral pills or creams to apply to the sores are indicated; medicines in injection form are also recommended.
- Blisters and sores should not be touched, rubbed, or scratched.
- To keep lips from drying out, apply moisturising creams, lip balms, or creams.
- To minimise redness and crusting, apply cold compresses.
Vitiligo

It’s a condition in which the cells that produce melanin either cease working or die. Caused by the loss of skin tone, this might result in uneven areas of skin that are pale. This illness is not contagious, invasive, or deadly. Spotty skin on the face, lips, or even the eyes and hair, on the other hand, can cause shame and psychological distress. The condition is classified as an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system assaults and destroys melanocytes.
Cause
- Although the exact cause is unknown, it is hereditary.
- It’s an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks our pigment-producing cells.
- It could appear as a result of stress, excessive sun exposure, or chemical exposure.
Treatment
- Treatments and procedures try to level out or restore the skin’s colour, which may or may not be permanent.
