 " title="Fractures: Types, Symptoms, Causes & More
" decoding="async" />
" title="Fractures: Types, Symptoms, Causes & More
" decoding="async" />Table of Contents
What is a fracture?
A fracture refers to the fracture of a bone in one area. A fracture may be partial or complete. Fractures can be divided into two categories:
Open fracture: This occurs when a broken bone is visible with a deep wound or a broken bone pierces the skin. It is also known as a compound fracture.
Clogged fractures: This occurs when there is a fracture of the bones and overcrowded skin
Types of Fractures
Fractures are of various kinds. Some of the most common types of fractures are the following:
Joint fracture: This type of fracture occurs when a bone is broken into several pieces
Greenstick fracture: This is a partial fracture or partial fracture, in which a bone is broken, from one side to the other.
Hairline breakage or pressure fractures: Excessive movement or excessive use of muscle puts pressure on the surrounding bones leading to fracture fractures. This is especially true for athletes.
Hairline fracture Damage Treatment: The most important thing you can do to cure stress fractures is to relax. Take a break from exercise. Depending on the severity of the injury, your doctor may recommend a period of rest. Also, freeze the injury area for up to 20 minutes at a time, several times a day, and keep the foot or leg high.
Avulsion fracture: When a piece of bone is separated by a large weight, it is known as an avulsion fracture. This is caused when a muscle or a muscle pulls on a bone.
Spinal fracture: When a bone breaks in a circular motion, it is called a fracture.
Flexible fractures: When a bone breaks in the opposite direction, it is called a transverse fracture.
Oblique fracture: As the name implies, fractures occur opposite the other side of the bone. Oblique fractures occur when the bone is broken at an angle. It usually occurs in long bones, such as the femur or tibia. This type of injury causes significant damage to the underside of the skin.
Oblique Fracture Treatment: Treatment varies depending on the severity of the injury. In the case of a minor fracture, conservative treatment (such as a bone marrow transplant) will suffice. However, there are cases where the bones need repair and surgery.
Line fracture: When a bone is broken along a long axis of the bone, it is called a line fracture.
Dislocated fracture: Here, the bone breaks into several pieces, causing the bone to lose its shape, causing a fracture from the site.
Pathological fracture: This type of fracture is caused by a disease that causes bone loss such as osteoporosis, bone cancer, etc.
Unstructured/stable fracture: If the fracture is severe enough for the pieces to be removed due to their position, it is known as a stable fracture.
Torus fracture: In this case, the affected bone is weakened, but not broken. Also known as buckle fracture, it causes pain but is a stable fracture. It is usually the most common fracture among children.
Stable Fractures
This is the type of fracture that occurs when an injury causes a bone to break, with its parts parallel. This means that the bone retains its original position.
Treatment of Stable Fractures: Since this type of fracture does not need to be repaired, the doctor will simply block the bone with a frame. The patient can take anti-inflammatory drugs without a counter to relieve pain.
Causes of fractures
Fractures occur when excessive force is applied to a bone that cannot withstand it. This force can be used by accident or fall, causing trauma to the affected area. Fractures may be the result of some orthopedic medical conditions such as osteoporosis or bone cancer. The bones are the weakest link in the chain.
Symptoms of a fracture – The symptoms of a fracture vary greatly between individuals. Not all symptoms can be present in everyone. Some of the most common symptoms of a fracture are the following:
Crepitus, abnormal movement, inflammation of the affected limb, pain, paralysis.
Diagnosis of fractures usually follows the procedure below:-
Physical examination: The doctor will carefully examine the affected area to understand the underlying cause of the symptoms.
Medical history inquiry: The doctor will inquire about medical history. This will help her to see if the existing symptoms could be caused by one of those health conditions.
Medical examination: The doctor may recommend the following diagnostic tests:-
X-ray: This X-ray examination creates a two-dimensional image of fragments of bones using electric beams.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This imaging technique uses radio waves to produce accurate images of bones, organs, and tissues.
CT or CAT (Computer Tomography) scan: This uses X-rays to produce detailed images of the opposite part of fragments of the affected area on a computer, and then to be re-scanned. This is also helpful in diagnosing stress or hair loss.
Bone scan: A thesis scan is considered to be very effective in diagnosing fractures, even those that may not be visible on X-ray. This scan usually requires 2 times, 4 hours apart, to take pictures of the affected area.
Treatment of fractures
The main motivation for fracture treatment is to reassemble the fractured limb, giving it time to heal, control pain, and prevent fractures from occurring in the same place.
Here are the different treatments offered:-
Medication: Analgesics may be prescribed to keep pain under control.
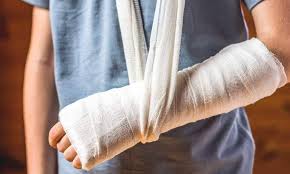
Cast or splint: This may be recommended to keep the affected area from moving. It provides much-needed support for fractures, especially during minimal movement. It also helps to keep the bone straight.
Pulling: This usually involves using weights, cords, and pulleys to stretch and pull certain muscles and tendons around the fracture. These weights, pulleys, and ropes, as well as a metal frame, are mounted on or over the bed. This helps to bind the bone, gradually increasing the healing process.
Surgery: This may be recommended when the type of fracture is similar to that the pieces of bone should be stitched together in their original position. Surgery, in such cases, can be of two types, depending on the type of fracture:
Internal Repair: This involves repairing broken bones with plates or metal rods inside the bone to align the bones accurately.
External repairs: In contrast to internal repairs, external repairs are installed outside the body to repair the required bones.
Despite these steps, it takes months for the fracture to subside as it takes time for new bones to grow between the pieces of bone and to bind the broken parts together.