 " title="Fatty Liver Symptoms, Causes, Treatment.
" decoding="async" srcset="https://www.medrot.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Fatty-Liver.jpg 1430w, https://www.medrot.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Fatty-Liver-300x169.jpg 300w, https://www.medrot.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Fatty-Liver-1024x576.jpg 1024w, https://www.medrot.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Fatty-Liver-768x432.jpg 768w" sizes="(max-width: 1430px) 100vw, 1430px" />
" title="Fatty Liver Symptoms, Causes, Treatment.
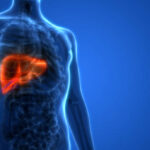
" decoding="async" srcset="https://www.medrot.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Fatty-Liver.jpg 1430w, https://www.medrot.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Fatty-Liver-300x169.jpg 300w, https://www.medrot.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Fatty-Liver-1024x576.jpg 1024w, https://www.medrot.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Fatty-Liver-768x432.jpg 768w" sizes="(max-width: 1430px) 100vw, 1430px" />Fatty liver, also known as steatohepatitis, is a condition in which fat accumulates in the liver and leads to inflammation. Small levels of fat in the liver are acceptable; but, excess of it could lead to a variety of health issues. The liver aids in the digestion of nutrients from food and liquids as well as the removal of toxic compounds from the bloodstream.
If you consume excess fat than you normally do, your liver may get inflamed. Your liver could well be impacted and damaged as a result of this. That is why you should consume a balanced level of fat in your meals or else you might risk your health.
Table of Contents
What is Fatty Liver?
The liver, our system’s second-biggest organ is essential for several vital processes. A fatty liver is caused by the accumulation of fat in the liver. It’s normal to have a modest amount of body fat in your liver. A fatty liver is defined as a buildup of fat in the liver that is unhealthy. A buildup of fatty tissue could lead to several disorders, notably liver cancer, cirrhosis, scarring, and final-stage liver disease.
Types based on causes
The disease is divided into two primary types based on its causes: alcoholic and non-alcoholic. Whereas alcoholic fatty liver occurs because of excessive alcohol consumption, the non-alcoholic fatty liver could be triggered by a mixture of other reasons. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is a term used to characterize fatty liver in persons who do not drink alcohol. Drinking is among the most likely reasons for fatty liver.
Alcohol consumption within limits might not always induce liver diseases, but excessive alcohol consumption can cause the liver to slow down and lead to illnesses like fatty liver. Inheritance, according to studies, plays a role in the progression of fatty liver. This could happen in one of two ways. Genetic factors may have a role in determining whether or not a person develops alcoholism. The rate of alcohol metabolism varies from person to person depending on genetic factors. Alcoholism, when paired with other variables like a high-fat diet, obesity, and other liver disorders, might raise the risk of getting the disease.
Causes of Fatty liver
When our body system is not able to adequately metabolize fat or produces far too much fat, fatty liver occurs. Extra fat is deposited in liver cells and aggregates in the liver. The chief reasons for fatty liver are excessive drinking and alcohol abuse. Though there are many reasons which can cause Fatty liver problems so let’s find out what are those reasons:
Insulin resistance
Insulin is a hormone released into your blood by your pancreas whenever you eat. It makes it possible for glucose from your meal to reach your cells and be utilized for energy. Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body’s insulin does not act effectively. When insulin fails to function effectively, only a low level of glucose gets burnt while more of it gets deposited to form fat. The liver produces additional fat, which contributes to the formation of fatty liver and the buildup of fat mass.
Medication
Several medicines, especially those taken for a long time, might lead to the formation of fatty liver. Anti-inflammatory pharmaceuticals, pain relievers, immunosuppressants, and cholesterol-lowering medications are among the most common offenders. If you’re on long-term medicine, every time talk to a doctor to see if it can harm your liver. If they do, get a regular liver function analysis done, and if any harm is discovered, talk with your doctor to switch your drugs to a certain liver-friendly one.
Addiction to carbohydrates
Sugar overloads the liver when you consume a lot of sugar and carbohydrate-rich foods. Because too much sugar in the blood is dangerous, your liver sought to defend you by converting it to fat. Endorphins and dopamine are released when sugar is consumed. It can be used as a calming agent. The most difficult part of quitting sugar is getting started. Temptations and cravings just last very few days, therefore it’s best to cut back on sugar for a healthier lifestyle.
Viruses
Chronic liver inflammatory is a side effect of hepatitis B and C. Fatty liver is the most common symptom of inflammation, although it can develop into cirrhosis or liver cancer over time. Hepatitis C seems to be more likely to cause this. Many persons with hepatitis C develop insulin resistance over time. This usually results in fat retention around the torso that is difficult to shift. Relatively mild viruses, such as Epstein Barr and CMV, can also cause fatty liver and liver inflammation.
Fatty liver diseases can also be caused by medical diseases such as PCOS, hypothyroidism, and excessive cholesterol levels.
Fatty liver is more likely in people who have HIV, hepatitis C, or inflammatory bowel disease.
During pregnancy, acute fatty liver can occur, which is a dangerous illness that can damage both the mother and the fetus.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver
Fatty liver disease can lead to consequences such as liver scarring in certain persons. Liver fibrosis is the scarring of the liver. Cirrhosis is a possibly serious disorder that could lead to liver collapse if you have significant liver fibrosis. Cirrhosis causes lifelong liver failure. That is why preventing it from forming in the very first place is so critical.
Symptoms of fatty liver are
- The majority of people are unaware that they have a fatty liver until the symptoms get more severe.
- General exhaustion and a sensation of fullness on the right side or in the center of the abdomen
- Underneath the skin, there are apparent, dilated blood vessels and a bloated belly.
- The skin and eyes have a yellowish color to them.
- Elevated levels of liver enzymes
- The feeling of vomiting
- Abdominal pain that is moderate to severe
- Appetite loss.
- As estrogen shields the liver and maintains insulin sensitivity, menopause can raise your chance of developing fatty liver. The widening waist, excess weight, and decreased energy levels, all of which cause you to exercise less, all raise your risk of storing more fats in your liver.
- Acute fatty liver of pregnancy is a type of fatty liver disease that affects pregnant women. They may encounter stomach pain, a loss of appetite, and excessive exhaustion, jaundice\nausea. If you’re pregnant and you’re having these symptoms, you should consult a doctor right away. Acute fatty liver in pregnancy can indeed be life-threatening, therefore it’s critical to get it diagnosed and treated as soon as possible.
Fatty liver disease: Stages
Simple fatty liver – This is a stage in which fat deposits in the liver cells are generally innocuous.
Non-alcoholic NASH (nonalcoholic steatohepatitis) occurs when the liver is damaged and inflamed. Obese or diabetic folks are more likely to experience it.
Fibrosis is a condition that develops when chronic inflammation induces scar tissue to form around the liver and adjacent blood vessels. The liver, on the other hand, continues to operate normally.
Cirrhosis is a condition in which normal liver tissues are overtaken by fibrosis to the point where the liver’s normal functioning is compromised. It can lead to cancer and liver failure.
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver
Your doctor will collect your medical records, perform a physical exam, and prescribe one or even more tests to identify fatty liver.
Physical Test
Your doctor may check or press on your abdomen to look for liver inflammation. They may be able to tell if your liver is swollen.
It is conceivable, though, for your liver to be inflammatory but not enlarged. By palpation, your doctor may not be able to identify if your liver is inflamed.
Blood Test
You’ll be advised to take a blood test if you’ve established noticeable symptoms of liver disease.
Inflammation in the liver is indicated by elevated liver enzymes. Fatty liver disease is one cause of liver inflammation, but it is far from the only one.
If your test results show that your liver enzymes are high, your doctor will probably order more testing to figure out what’s causing the inflammation.
Imaging Tests
To examine for fat deposits or other abnormalities with your liver, the doctor may perform one or more of the imaging procedures listed below:
- Ultrasound examination
- X-rays
- Magnetic resonance imaging
A test known as vibration-controlled transient elastography may also be ordered (VCTE, FibroScan). Low-frequency sound waves are used to detect liver stiffness in this examination. It can aid in the detection of scarring.
Biopsy of the liver
The best way to identify the degree of liver disease is to do a liver biopsy. A doctor will introduce a needle into your liver and extract a bit of tissue for examination during a liver biopsy. They will administer a local anesthetic to alleviate the discomfort. This test might help you figure out if you have fatty liver disease or scarring in your liver.
Treatment of Fatty Liver
Fatty liver is presently the subject of extensive investigation in the medical field. Various drugs, as per the researchers, could help minimize liver inflammation. Metformin, rosiglitazone, and betaine are among them. Another drug under investigation is Xenical, which prevents some fat from being absorbed from your food.
There is presently no therapeutic option for fatty liver, but research is ongoing. Maintaining your blood sugar, lowering weight, maintaining your cholesterol, reducing sugar and saturated fat intake, and minimizing or eliminating alcoholic drinks can all help you avoid getting the condition or its progression.
Fatty liver disease is becoming more common as the number of diabetics and obese people increases. Regular exercise and a well-balanced diet low in fats, sweets, and carbohydrates can help to avoid non-alcoholic liver problems to some level. Those who have untreated medical issues must seek treatment. Maintain a healthy lifestyle to avoid fatty liver disease, which can progress over time if not addressed early on.
If you have a fatty liver as a result of poor food patterns or obesity, your doctor may advise you to include particular foods in your diet. Losing weight and healing your liver can both be accomplished by reducing your calorie intake. Physical activity should be increased as well.
What to eat if you have fatty liver?
Coffee consumers have been demonstrated to have less liver harm in the long run than non-coffee drinkers. One cup of black coffee every day is an excellent approach to help your liver stay healthy.
Avocado is a healthy fat that is low in saturated fat. It’s also a good substitute for saturated fat items, which you should limit if you have a fatty liver.
Frequent consumption of n a whey protein shake will help you maintain your fatty liver under control. As per the doctors, taking a scoop of whey protein after a workout is the greatest method to get the most out of it.
Green tea contains antioxidants that are beneficial to your liver. Catechins, a type of antioxidant, aid in the reduction of liver fat and inflammation in persons with NAFLD.
Unsaturated fats, such as olive oil, help persons with NAFLD lose weight. For those with a fatty liver, maintaining a healthy weight is essential.
Maintain a healthy diet. Make an effort to include items from all food groups in your diet. Fresh fruits and vegetables, entire grains, lean proteins, low-fat dairy, and healthy fats and oils are all examples of this. Reduce your calorie intake. Make an effort to reduce your intake of high-calorie foods. Concentrate on fiber. Fiber can aid in the improvement of liver function. Fresh fruits and vegetables, lentils, and whole grains are examples of fiber-rich foods.
Certain foods should be avoided or limited to reduce fatty liver. Sugary foods, fried foods, salt, white bread, rice, pasta, and alcohol are just a few examples. Before you try a new supplement or any therapy, always with your specialist. Certain supplements and natural cures may put your liver under strain or conflict with prescriptions you’re taking.